On July 2, 2025, Chinese authorities approved their first new food ingredient involving genetically modified microorganisms in its production process – D-psicose. This approval signals a positive trend in the development of synthetic biology in the food ingredient industry.
The Department of Food Safety Standards and Monitoring Evaluation of the National Health Commission released the Announcement on D-psicose and 19 other new food ingredients (2025 No. 4). This announcement includes five new food raw materials, nine new food additives, and six new food-related products. Among these, D-psicose is undoubtedly the most notable new food ingredient in this announcement. It is a highly anticipated strategic sweetener, its approval will quickly open up the domestic market and significantly enrich product formula options.

The announcement includes two production processes for the approved D-psicose:
Process One involves using glucose or sucrose as raw materials, which are then fermented, purified, and dried using E. coli AS10.
Process Two uses fructose as the raw material, which is catalyzed by the permitted D-psicose 3-epimerase, followed by processes of decolorization, separation, purification, and crystallization.
Both the product from Process Two and the permitted D-psicose 3-epimerase are being submitted by CIRS Group. The official announcement of D-psicose 3-epimerase in May 2023 marks its first approval in China.
D-psicose: A Natural, Low-Calorie Sugar Substitute with Promising Potential
D-psicose is a natural, low-calorie hexacarbon ketose that has gained significant recognition for its value as a sugar substitute. It is widely used in the food, beverage, and seasonings in the international market, with mature production and application technologies. Its key advantages include:
- Reducing calorie intake and aiding in sugar and fat control. When ingested orally, most D-psicose is absorbed by the small intestine, with 70% ultimately excreted through urine; the remaining unabsorbed portion enters the large intestine, where only a small amount is fermented by intestinal microorganisms into short-chain fatty acids, while the rest is excreted with feces. After absorption in the intestine, D-psicose does not participate in glucose-related metabolism or energy production. FDA stated D-psicose does not need to be included in the “total sugars” or “added sugars” on food nutrition labels. For calorie calculation, it is counted at only 0.4 kcal/g-1. Meanwhile, Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, in Notification No. 2 of Seishoku-hatsu 0331, permits the use of D-psicose and stipulates its energy value as 0 kcal/g.
- It has a taste similar to sucrose and is widely used in various applications, making it an ideal sugar substitute. D-psicose has a mild and pure taste, with minimal off-flavors and good solubility. This makes it ideal for beverages, yogurts, and other water-based foods where steviol glycosides and erythritol often have issues with poor solubility and a bitter aftertaste. Additionally, D-psicose is the only sugar substitute that can undergo caramelization, enhancing the sensory quality of baked goods like bread and cookies.
- It can fulfill physiological functions and meet the health needs of different groups. D-psicose does not participate in human metabolism and has extremely low calories, perfectly aligning with the “0 sugar” claim. Furthermore, extensive research has shown that it has clinical value in regulating blood pressure and reducing the risk of high-sugar diet-related diseases such as diabetes, obesity, and dental caries. In the current trend of healthy sugar reduction that is reshaping the sugar substitute market, D-psicose can meet the health needs of different groups by developing a variety of sugar substitutes.
In summary, D-psicose has gained significant attention in the industry due to its advantages. It is expected to quickly enter the domestic market and diversify product formulations after its official launch.
The Compliance Journey of D-psicose in China
Before this announcement, D-psicose had already received regulatory approval in multiple countries and regions, including the United States, Canada, Australia-New Zealand, Japan, and South Korea. In China, there are seven records of its acceptance (including one overseas product). The primary method for industrial production of D-psicose is through biological enzyme conversion, with the core enzyme, D-psicose 3-epimerase, also having three approved versions (all submissions were handled by CIRS Group). This indicates that several companies in China have mature production technologies and large-scale production capacities, actively promoting the compliance of D-psicose and related enzyme preparations domestically.
Additionally, the long compliance process of D-psicose in China demonstrates that the authorities have thoroughly investigated its safety, considering aspects such as production processes, quality specifications, and consumption levels, reflecting a cautious and scientific approach.
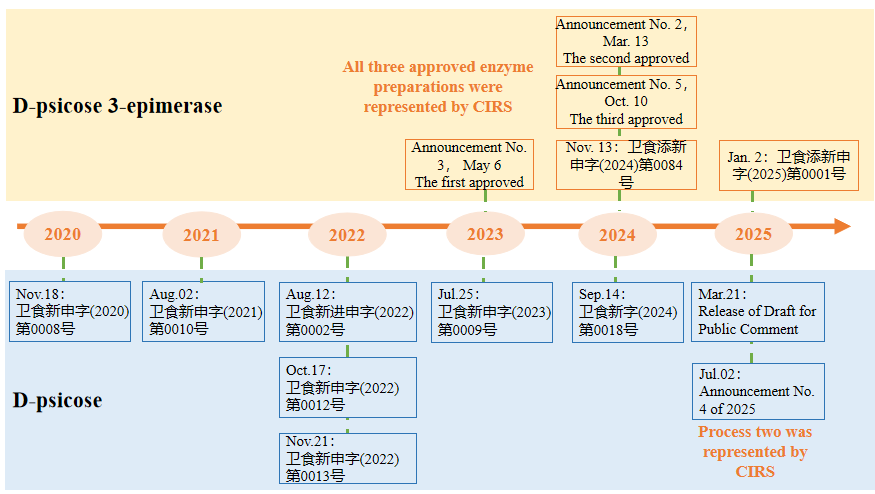
D-psicose and D-psicose 3-epimerase acceptance and compliance information in China
(data from the official website of the National Health Commission)
CIRS Insights
D-psicose, a new type of sugar substitute with extremely low calories, excellent water solubility, and the ability to ensure or enhance food sensory quality, as well as perform various physiological functions, is expected to see widespread application in the food industry after regulatory approval. As the first genetically modified microorganism-produced new food ingredient announced in China, this approval is a significant boost for companies in synthetic biology, offering new opportunities for industry innovation and industrialization!
About CIRS Group
Established in 2012, the Food Business Division of CIRS Group has helped over 1,000 domestic and international food companies achieve one-stop compliance solutions. CIRS offers a full range of regulatory services covering novel food applications, synthetic biology-derived foods, U.S. GRAS notice, EU novel food application, health food registration, and food for special medical purposes (FSMP).
Our food services in China include but not limited to:
- China new food raw materials registration
- China new food additive registration
- China health food (dietary supplement) registration/filing
- China health food testing service
- China new food contact substance registration
- China food for special medical purpose (FSMP) registration
- China infant formula milk powder registration
If you need any assistance or have any questions, please get in touch with us via service@cirs-group.com.

