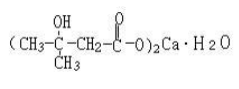As of July 2, 2025, China’s National Health Commission (NHC) has issued a total of three announcements regarding “three new” food products (Announcements No. 1, No. 3, and No. 4 of 2025). These announcements approved a total of 51 products, including new food raw materials, new food additives, and food-related products. Among them, 12 were approved as new food raw materials: Stevia polyphenols, Lemon myrtle leaves, Maqui berry anthocyanins, Wheat polar lipids, Calcium β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (CaHMB), Cherry blossom polyphenols, Rye pollen, D-allulose, Saccharomyces cerevisiae CNCM I-3799, Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BLa80, Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis LMG11588, Sodium hyaluronate (extraction method).

In addition, according to the official websites of the NHC and the China National Center for Food Safety Risk Assessment (CFSA):
- 33 new food raw material applications were accepted;
- 8 draft proposals for new food raw materials were released for public comment;
- 6 substances had their technical review process terminated;
- No administrative decisions were issued denying approval of any new food raw material.
Below is an overview of the acceptance and approval status of new food raw materials in China during the first half of 2025:
List of Accepted New Food Raw Materials
As of July 2, 2025, the NHC has publicly accepted 33 applications for new food raw materials (including 26 domestic and 7 imported products). The technical review status of each product is shown in the following table:
No | Date of acceptance | Filing number | Name | Review status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2025-01-06 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0001号 | Plant sterols | 2025-05-29 Extension notice |
| 2 | 2025-01-17 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0002号 | Krill oil | 2025-05-29 Extension notice |
| 3 | 2025-01-22 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0003号 | Brown algae oligosaccharides | 2025-02-21 Extension notice |
| 4 | 2025-01-24 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0004号 | Saussurea involucrata cell culture | 2025-05-29 Extension notice |
| 5 | 2025-01-24 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0005号 | Ergothioneine | 2025-05-29 Extension notice |
| 6 | 2025-01-24 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0006号 | L-theanine | 2025-05-29 Extension notice |
| 7 | 2025-02-05 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0007号 | Sericin protein | 2025-05-29 Extension notice |
| 8 | 2025-02-06 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0008号 | N-acetylneuraminic acid | 2025-02-21 Extension notice |
| 9 | 2025-02-06 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0009号 | β-lactoglobulin (non-animal sourced) | 2025-03-31 Extension notice |
| 10 | 2025-02-07 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0010号 | Fusarium venenatum protein | 2025-02-21 Extension notice |
| 11 | 2025-02-08 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0011号 | Lactobacillus paracasei N1115 | 2025-03-31 Extension notice |
| 12 | 2025-02-10 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0012号 | L-ergothioneine | 2025-05-29 Extension notice |
| 13 | 2025-02-11 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0013号 | Cyclocarya paliurus leaf extract | Not issued for public comments yet |
| 14 | 2025-02-14 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0014号 | Hericium erinaceus mycelium (strain BCRC 35669) | 2025-03-31 Recommend not granting approval |
| 15 | 2025-02-18 | 卫食新进申字(2025)第0001号 | Bifidobacterium bifidum BGN4 | 2025-03-31 Extension notice |
| 16 | 2025-03-03 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0015号 | Green coffee bean extract | 2025-03-31 Extension notice |
| 17 | 2025-03-11 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0016号 | Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis YLGB-1496 | 2025-03-31 Extension notice |
| 18 | 2025-03-20 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0017号 | L-α-glycerylphosphorylcholine | 2025-03-31 Extension notice |
| 19 | 2025-03-24 | 卫食新进申字(2025)第0002号 | Proanthocyanidins | 2025-03-31 Extension notice |
| 20 | 2025-04-22 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0019号 | Cyclocarya paliurus leaf extract | 2025-05-29 Extension notice |
| 21 | 2025-04-27 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0020号 | Taurine-conjugated bile acids complex | 2025-06-05 Recommend not granting approval |
| 22 | 2025-05-09 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0021号 | Bacillus subtilis natto VB205 | 2025-05-29 Extension notice |
| 23 | 2025-05-21 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0022号 | Fusarium venenatum TB01 strain fermented mycelial protein | 2025-05-29 Extension notice |
| 24 | 2025-05-21 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0023号 | Vine tea polyphenols | 2025-05-29 Extension notice |
| 25 | 2025-05-22 | 卫食新进申字(2025)第0003号 | Glucosyl hesperidin | 2025-06-05 Extension notice |
| 26 | 2025-05-23 | 卫食新进申字(2025)第0004号 | Tuna anserine | 2025-06-05 Extension notice |
| 27 | 2025-05-23 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0024号 | N-acetylneuraminic acid | 2025-06-05 Extension notice |
| 28 | 2025-05-23 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0025号 | Chlorella protothecoides (yellow) | 2025-06-05 Extension notice |
| 29 | 2025-06-03 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0026号 | Cyclocarya paliurus leaf extract | Not issued for public comments yet |
| 30 | 2025-06-19 | 卫食新申字(2025)第0027号 | Krill oil | Not issued for public comments yet |
| 31 | 2025-06-24 | 卫食新进申字(2025)第0005号 | Banana blossom | Not issued for public comments yet |
| 32 | 2025-06-26 | 卫食新进申字(2025)第0006号 | Streptococcus salivarius K12 | Not issued for public comments yet |
| 33 | 2025-06-26 | 卫食新进申字(2025)第0007号 | Streptococcus salivarius M18 | Not issued for public comments yet |
New Food Raw Materials Released for Public Comments by CFSA in the First Half of 2025 (8 in Total)
As of July 2, 2025, a total of eight new food raw materials had passed technical review by the Expert Review Committee and were released for public comments by CFSA in the first half of the year. The remaining four materials—D-allulose, Saccharomyces cerevisiae CNCM I-3799, Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BLa80, and Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis LMG 11588—have already been formally approved. For details, see Section 3 of this article. The relevant announcements are as follows:
Olive fruit polyphenols
Name | Olive fruit polyphenols |
Basic information | Source: Oleaeuropaea L. |
Production process | Made from the fruit of Oleaeuropaea L. as the raw material, it is processed through ethanol extraction, filtration, concentration, degreasing, drying, and pulverization. |
Recommended level | ≤600 mg/day (calculated based on a total polyphenol content of 10 g/100 g; for higher concentrations, the dosage should be adjusted proportionally to the actual content). |
Note | 1. Scope of use and maximum dosage: - dairy and dairy products: modified milk and flavored fermented milk (0.5 g/kg), modified milk powder calculated based on the reconstituted liquid mass, cheese, processed cheese, cheese products, and condensed milk calculated based on the multiplication factor of raw milk. - beverages: liquid beverages ≤50 mL packaging (5 g/kg), 51–500 mL packaging (0.5 g/kg), and solid beverages calculated based on the reconstituted liquid mass. - jelly: 8 g/kg. - cocoa products, chocolate, and chocolate products(including cocoa butter substitute products): 8 g/kg. - candy: 25 g/kg. - frozen desserts: 5 g/kg. - alcoholic beverages: 2.5 g/kg. - preserved fruits: 5 g/kg. 2. Infants, pregnant women, and lactating women should avoid consumption. Labels and instructions must clearly indicate the unsuitable populations and consumption limits. 3. Quality standards and food safety indicators refer to the appendix. |
Lutein esters
Name | Lutein esters |
Basic information | Source: Tagetes erecta L. Structure formula: CAS No.:547-17-1 Molecular formula: C72H116O4 relative molecular mass: 1045.71 |
Production process | Made from Tagetes erecta L. as the raw material, it is processed through dehydration and crushing, solvent extraction, low molecular weight alcohol purification and vacuum concentration. |
Recommended level | ≤ 36 mg/day (calculated based on Helenien content). |
Note | 1. Scope of use: bakery products, dairy products, beverages, ready-to-eat cereals, frozen beverages, condiments and confectionery, excluding foods for infants and young children. 2. The information related to Helenien in the original Ministry of Health Announcement No. 12 of 2008 is abolished. 3. Quality standards and food safety indicators refer to the appendix. |
Camelina seed oil
Name | Camelina seed oil |
Basic information | Source: seeds of Camelina sativa (L.) Crantz |
Production process | Made from seeds of Camelina sativa (L.) Crantz, it is produced through processes such as screening, pressing, precipitation, and filtration. |
Note | 1.The scope of use does not include infant foods. 2.Food safety indicators shall comply with the current national food safety standards of China for vegetable oils and fats. |
Elderberry anthocyanins
Name | Elderberry anthocyanins |
Basic information | Source: Sambucus nigra L. |
Production process | Made from fruits of Sambucus nigra L., it is produced through processes such as enzymatic hydrolysis, pressing, membrane filtration, sterilization, and drying. |
Recommend intake | < 3.2 g/day (calculated based on a total anthocyanin content of 10 g/100 g; if the actual content exceeds this level, the intake should be adjusted accordingly). |
Note | 1.Scope of use and maximum dosage: - dairy and dairy products: modified milk and flavored fermented milk (3.2 g/kg), modified milk powder calculated based on the reconstituted liquid mass, cheese, processed cheese, cheese products, and condensed milk calculated based on the multiplication factor of raw milk. - beverages: liquid beverages ≤50 mL packaging (32 g/kg), 51–500 mL packaging (3.2 g/kg), and solid beverages calculated based on the reconstituted liquid mass. - jelly: 56 g/kg. -cocoa products, chocolate, and chocolate products(including cocoa butter substitute products): 56 g/kg. - candy: 160 g/kg. - frozen desserts: 32 g/kg. - Baked goods: 16 g/kg. - alcoholic beverages: 16 g/kg. 2. Infants, pregnant women, and lactating women should avoid consumption. Labels and instructions must clearly indicate the unsuitable populations and consumption limits. 3. Quality standards and food safety indicators refer to the appendix. |
New Food Raw Materials Approved in 2025 (12 in Total)
As of July 2, 2025, a total of 12 new food raw materials had been officially approved by NHC in 2025. Among them, rye pollen was previously approved as a new food raw material under Announcement No. 3 of 2023. However, due to evolving industry needs, the latest announcement adjusted the dietary fiber content requirements, rendering the original announcement invalid. Detailed approval information for each product is as follows:
Stevia polyphenols
Name | Stevia polyphenols |
Basic information | Source: leaves of stevia polyphenols |
Brief introduction of production process | Made from the leaves of stevia polyphenols through processes such as ethanol extraction, filtration, purification, concentration, and drying. |
Recommended intake | ≤500 mg/day |
Other information | 1. Scope of use and maximum use level: -Milk and dairy product: modified milk and flavored fermented milk 0.5 g/kg; modified milk powder is calculated based on the reconstituted liquid mass; cheese, processed cheese, cheese products, and condensed milk are calculated based on the multiple of raw milk. -Beverages: liquid beverages ≤50 mL packaging: 5 g/kg; 51-500 mL packaging: 0.5 g/kg; solid beverages are calculated based on the reconstituted liquid mass. -Jelly: 8 g/kg. -Cocoa products, chocolate, and chocolate products (including cocoa butter substitutes and products): 8 g/kg. -Candies: 25 g/kg. -Frozen desserts: 5 g/kg. -Alcoholic beverages: 2.5 g/kg. -Preserved fruits: 5 g/kg. 2. Not suitable for infants, pregnant women, and lactating women. Labels and instructions must indicate unsuitable populations and consumption limits. 3. Quality specifications and food safety indicators are listed in the appendix. |
Lemon myrtle leaf
Name | Lemon myrtle leaf |
Basic information | Source: leaves of Backhousia citriodora F. Muell. |
Brief introduction of production process | Made from the leaves of Backhousia citriodora F. Muell. through processes such as picking, sorting, cleaning and drying. |
Other information | 1.Not suitable for infants, pregnant women, and lactating women. Labels and instructions must indicate unsuitable populations and consumption limits. 2.Food safety indicators are listed as follow. |
Maqui berry anthocyanins
Name | Maqui berry anthocyanins |
Basic information | Source: fruits of aristoteliachilensis |
Brief introduction of production process | Made from the fruits of aristoteliachilensis through processes such as extraction, filtration, purification, concentration, and drying. |
Recommended intake | ≤900 mg/day |
Other information | 1. Scope of use and maximum use level: -Milk and dairy product: modified milk and flavored fermented milk 0.8 g/kg; modified milk powder is calculated based on the reconstituted liquid mass. -Beverages: liquid beverages ≤50 mL packaging: 8 g/kg; 51-500 mL packaging: 0.8 g/kg; solid beverages are calculated based on the reconstituted liquid mass. -Jelly: 14 g/kg. -Cocoa products, chocolate, and chocolate products (including cocoa butter substitutes and products): 14 g/kg. -Candies: 40 g/kg. -Frozen desserts: 8 g/kg. -Bakeed food: 4 g/kg. -Alcoholic beverages: 4 g/kg. 2. Not suitable for infants, pregnant women, and lactating women. Labels and instructions must indicate unsuitable populations and consumption limits. 3. Quality specifications and food safety indicators are listed in the appendix. |
Wheat polar lipids
Name | Wheat polar lipids |
Brief introduction of production process | Made from wheat flour through processes such as ethanol extraction, acetone precipitation, separation, drying and grinding. |
Recommended intake | ≤30 mg/day (calculated based on a digalactosyldiacylglycerol content of 40g/100g. If the content exceeds this amount, it will be converted according to the actual content.) |
Other information | 1. Scope of use and maximum use level: -Beverages: liquid beverages ≤50 mL packaging: 0.6 g/kg; 51-500 mL packaging: 0.06 g/kg; solid beverages are calculated based on the reconstituted liquid mass. 2. Not suitable for infants, pregnant women, and lactating women. Labels and instructions must indicate unsuitable populations and consumption limits. 3. Quality specifications and food safety indicators are listed in the appendix. |
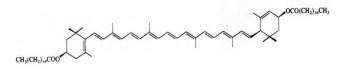
Calcium β-hydroxy-β-methyl butyrate (CaHMB)
Name | Maqui berry anthocyanins |
Basic information | Structure: Molecular formua: C10H18O6Ca∙H2O Molar mass: 292 |
Brief introduction of production process | Made from sodium hypochlorite, diacetone alcohol, hydrochloric acid, ethyl acetate, ethanol, and calcium hydroxide as the main raw materials, through processes such as oxidation synthesis, acidification, extraction, neutralization reaction, centrifugation, and drying. |
Recommended intake | ≤6 mg/day |
Other information | 1.Scope of use: beverages, milk and diary products, cocoa products, chocolate and chocolate products, candies, bakeed food, sports nutrition products, and FSMPs. 2.Not suitable for infants, pregnant women, and lactating women. Labels and instructions must indicate unsuitable populations and consumption limits. 3.Quality specifications and food safety indicators are listed as follow. |
Sakura polyphenols
Name | Sakura polyphenols |
Basic information | Source: flowers of Prunusserrulata var. lannesiana (Carrière) Makino |
Brief introduction of production process | Made from the flowers of Prunusserrulata var. lannesiana (Carrière) Makino through processes such as ethanol extraction, filtration, purification, concentration, drying, and pulverization.. |
Recommended intake | ≤350 mg/day |
Other information | 1.Scope of use and maximum use level: -Milk and dairy product: modified milk and flavored fermented milk 0.35 g/kg; modified milk powder is calculated based on the reconstituted liquid mass; cheese, processed cheese, cheese products, and condensed milk are calculated based on the multiple of raw milk. -Beverages: liquid beverages ≤50 mL packaging: 3.5 g/kg; 51-500 mL packaging: 0.35 g/kg; solid beverages are calculated based on the reconstituted liquid mass. -Jelly: 7 g/kg. -Cocoa products, chocolate, and chocolate products (including cocoa butter substitutes and products): 7 g/kg. -Candies: 20 g/kg. -Frozen desserts: 4 g/kg. -Alcoholic beverages: 1.5 g/kg. -Preserved fruits: 4 g/kg. 2. Not suitable for infants, pregnant women, and lactating women. Labels and instructions must indicate unsuitable populations and consumption limits. 3. Quality specifications and food safety indicators are listed in the appendix. |
Rye pollen
Name | Rye pollen |
Basic information | Source: Secale CerealeL. |
Brief introduction of production process | Made from Secale CerealeL produced through a series of processes including pollen collection, drying, grinding, and sieving. |
Recommended intake | ≤1.5 g/day |
Other information | 1.Infants, young children, pregnant women, breastfeeding women, and individuals allergic to pollen should not consume this product. The label and instructions must indicate the groups for whom consumption is not recommended, as well as the intake limitations. 2.The information related to rye pollen in Announcement No. 3 of 2023 by the NHC has been rendered invalid. 3.Quality specifications and food safety standards are provided in the appendix. |
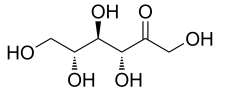
D-allulose/D-psicose
Name | D-allulose/D-psicose |
Basic information | Structure:
CAS No.: 551-68-8 Molecular formua: C6H12O6 Molar mass:180.16 |
Brief introduction of production process | Method One involves using glucose or sucrose as raw materials, which are then fermented, purified, and dried using E. coli AS10. Method Two uses fructose as the raw material, which is catalyzed by the permitted D-psicose 3-epimerase, followed by processes of decolorization, separation, purification, and crystallization. |
Recommended intake | ≤ 20 g/day |
Other information | 1. Not suitable for infants, pregnant women, and lactating women. Labels and instructions must indicate unsuitable populations and consumption limits. 2. Quality specifications and food safety indicators are listed in the appendix. |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae CNCM I-3799
Name | Saccharomyces cerevisiae CNCM I-3799 |
Other information | 1. The strain is approved and included in the List of Microorganisms That Can Be Used in Food, with the exception that it is not permitted for use in infant and young children’s food. 2. The food safety indicators shall comply with the requirements of the National Food Safety Standard for Microbial Preparations Used in Food Processing (GB 31639). |
Bifidobacterium animalis subsp.lactis BLa80
Name | Bifidobacterium animalis subsp.lactis BLa80 |
Other information | 1. The strain is approved and included in the List of Microorganisms That Can Be Used in Food, with the exception that it is not permitted for use in infant and young children’s food. 2. The food safety indicators shall comply with the requirements of the National Food Safety Standard for Microbial Preparations Used in Food Processing (GB 31639). Cronobacter spp. must not be detected (per 100 g). |
Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis LMG 11588
Name | Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis LMG11588 |
Other information | 1. The strain is approved and included in the List of Microorganisms That Can Be Used in Food, with the exception that it is not permitted for use in infant and young children’s food. 2. The food safety indicators shall comply with the requirements of the National Food Safety Standard for Microbial Preparations Used in Food Processing (GB 31639). Cronobacter spp. must not be detected (per 100 g). |
Sodium hyaluronate (extract)
Name | Sodium hyaluronate (extract) |
Basic information | Chicken comb from Gallus gallus domesticus |
Brief introduction of production process | The product is manufactured from the combs of Gallus gallus domesticus through a series of processes including chopping, enzymatic hydrolysis, filtration, concentration, purification, drying, and milling. |
Recommended intake | ≤ 300 mg/day |
Other information | 1.Scope of use: Dairy and dairy products: 0.3 g/kg for formulated milk and flavored fermented milk; for milk powder and its formulated products, the amount is calculated based on the reconstituted liquid mass. Beverages: For liquid beverages packaged in containers of ≤50 mL, up to 3.0 g/kg; for packaging between 51 mL and 500 mL, up to 0.3 g/kg; for solid beverages, the amount is calculated based on the reconstituted liquid mass. Alcoholic beverages: 1.5 g/kg. Cocoa products, chocolate and chocolate products (including compound chocolate and related products) and confectionery: 4.5 g/kg. Frozen desserts: 3.0 g/kg. 2.Not suitable for infants, pregnant women, and lactating women. Labels and instructions must indicate unsuitable populations and consumption limits. 3.Quality specifications and food safety indicators are listed as follow. |
Raw Materials Added to the Discontinued Review List in 2025 (6 in Total)
As of July 2, 2025, a total of six raw materials were newly added to the discontinued review list in the first half of the year. The list now includes 88 products in total.
Note: In general, when an applicant receives a determination of substantial equivalence, or when a material is managed as a regular food or a local specialty food, inclusion in the discontinued review list may be regarded as an alternative form of approval.
Pyrroloquinoline Quinone Disodium Salt
Product Name | Pyrroloquinoline Quinone Disodium Salt |
Review Comments | This product is produced by fermentation using the strain Hyphomicrobium denitrificans JCSS230201, followed by filtration, purification, decolorization, crystallization, and drying. It is substantially equivalent to the pyrroloquinoline quinone disodium salt approved in Announcement No. 8 of 2023. Except for the production process, all other requirements shall follow the previously approved specifications. |
Acceptance Date & Number | 2024-07-02卫食新申字(2024) No. 0013 |
Pyrroloquinoline Quinone Disodium Salt
Product Name | Pyrroloquinoline Quinone Disodium Salt |
Review Comments | This product is produced by fermentation using the strain Hyphomicrobium denitrificans MQ004-2, followed by filtration, purification, crystallization, and drying. It is substantially equivalent to the product approved in Announcement No. 8 of 2023, with all requirements—except for the production process—following the existing approved standard. |
Acceptance Date & Number | 2024-05-10卫食新申字(2024) No. 0006 |
Glutathione-Enriched Yeast (formerly Glutathione Yeast Powder)
Product Name | Glutathione-Enriched Yeast |
Review Comments | This product is derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae via culturing, fermentation, enzymatic hydrolysis, optional centrifugation, and drying. Its main components include protein and glutathione, along with fats, amino acids, and minerals. It shall comply with the standard GB/T 20886.2—2021 (Yeast Product Quality Requirements – Part 2: Processed Yeast Products). |
Acceptance Date & Number | 2024-07-19卫食新申字(2024) No.0015 |
Lianghe Yunnan Gleditsia
Product Name | Lianghe Yunnan Gleditsia |
Review Comments | As this product is traditionally consumed in certain local regions, it shall be managed in accordance with Article 29 of the Food Safety Law, and the review is terminated. |
Acceptance Date & Number | 2024-11-21卫食新申字(2024) No. 0021 |
N-Acetylneuraminic Acid
Product Name | N-Acetylneuraminic Acid |
Review Comments | This product is produced using the strain Escherichia coli SAIS107 (derived from E. coli BL21 (DE3); donor organisms include Pisum sativum, E. coli, and Campylobacter jejuni). It is made through fermentation with food-grade glucose and glycerol, followed by filtration, sterilization, and purification. The product is substantially equivalent to the N-acetylneuraminic acid approved in Announcement No. 7 of 2017, and thus the review is terminated. All relevant requirements of the previously approved product apply. |
Acceptance Date & Number | 2025-02-06卫食新申字(2025) No. 0008 |
Jujube Leaf (formerly Red Jujube Leaf)
Product Name | Jujube Leaf |
Review Comments | This product is derived from the leaves of Ziziphus jujuba Mill. (family Rhamnaceae). It contains carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and at least 1.0% total flavonoids. It has a long history of consumption across many Chinese provinces. The review is terminated, and the product may be used as a food ingredient—for infusion or as an ingredient in beverages. Food safety limits must be met, including:Lead (Pb) ≤ 5.0 mg/kg |
Acceptance Date & Number | 2024-11-26卫食新申字(2024) No. 0022 |
Insight from CIRS
In the first half of 2025, the number of accepted and approved new food raw material applications has already matched that of the entire year of 2024. As of July 2, 33 new food raw materials had been accepted—exceeding the total of 30 for all of 2024. At the same time, NHC officially approved 51 “Three New Food” products, including 12 new food raw materials, comparable to the full-year approval total for 2024. This reflects growing enthusiasm among enterprises, with increasing competition in strategic market layout for new food raw materials. Meanwhile, approval efficiency is also accelerating. For instance, Peach Leaf Extract and Cherry Blossom Polyphenols were approved in just nine months.
Emerging application trends: focus on plant extracts and edible microorganisms. Based on the lists of accepted, consulted, and approved applications, it is evident that functional extracts derived from plants and edible microbial strains are drawing heightened interest. Examples include Stevia polyphenols, polar wheat lipids, Maqui berry anthocyanins, Saccharomyces cerevisiae CNCM I-3799, and strains added to the List of Microorganisms Permitted in Infant and Young Children Foods, such as Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BLa80 and Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis LMG 11588. These innovations support the development of functional and diversified health foods, contributing to the advancement of the broader wellness industry.
D-Allulose officially approved – The first new food raw material involving genetically modified microorganisms. In September 2024, China issued the “Requirements for Safety Evaluation Dossiers of Genetically Modified Microorganisms for Food Processing (Trial)”, opening the application pathway for “Three New Food” products involving genetically modified microorganisms (GMMs). On July 2, D-Allulose became the first publicly announced and approved new food raw material in China whose production process involves GMMs, marking a milestone in the application of synthetic biology in the food sector.
This approval sets a precedent for the application of synthetic biology in food innovation, highlighting a key trend to watch for enterprises.
With years of experience in “Three New Food” applications and multiple successful cases, CIRS Group—as the agent for this D-Allulose application—offers extensive practical expertise. We welcome industry stakeholders to contact us for consultation on new food raw material applications.
About CIRS Group
Established in 2012, the Food Business Division of CIRS Group has helped over 1,000 domestic and international food companies achieve one-stop compliance solutions. CIRS offers a full range of regulatory services covering novel food applications, synthetic biology-derived foods, U.S. GRAS notice, EU novel food application, health food registration, and food for special medical purposes (FSMP).
Our food services in China include but not limited to:
- China new food raw materials registration
- China new food additive registration
- China health food (dietary supplement) registration/filing
- China health food testing service
- China new food contact substance registration
- China food for special medical purpose (FSMP) registration
- China infant formula milk powder registration
If you need any assistance or have any questions, please get in touch with us via service@cirs-group.com.
Note: There may be omissions and errors in the data and statistics. The data in this article is for reference only, please refer to the official information published by government departments.